SDG 17 and Sustainable Recovery

Key aspects of SDG 17:
1. Strengthen domestic resource mobilization; increase official development assistance; ensure debt sustainability; enhance international cooperation on science, technology and innovation (17.1, 17.2, 17.4, 17.6)
COVID-19 recovery that is fair, green and inclusive and involves investment in health, social protection, sustainable infrastructure and crisis preparedness, while directing the economic recovery along a significantly more sustainable and carbon-neutral trajectory and closing the digital divide will require significant resource mobilization.
Domestic resource mobilisation includes the raising of taxes through progressive tax regimes to ensure that states are able to comply with their obligation to raise the maximum available resources for the realization of human rights, including the right to health and the related access to healthcare and social security, which provide crucial services and safety nets in this context.
COVID-19 recovery, especially in low-income countries will require significant resource mobilization including from official development assistance. Yet, aid levels are decreasing, and donor countries have not lived up to their pledge to ramp up development finance.
The global COVID-19 pandemic has demonstrated the importance of strengthening coordination between countries. Sustainable recovery will require better multilateral and regional collaboration on many issues including data, technology innovation and transfer, closing the digital divide, sustainable finance, debt management, and crisis preparedness.
Sustainable response and recovery actions:
Progressive taxation is key to financing sustainable recovery. The tax burden needs to shift from low-income households and labour to wealthy individuals and corporations, ensuring that they pay a fair contribution to the provision of public services.
Donor countries must live up to their pledge to ramp up development finance.
Debt restructuring and relief is important for enhancing equality within and between countries and for allowing countries with limited resources to focus on combating the pandemic. International finance institutions must provide fiscal and policy space for governments to realise economic and social rights, as an essential part of recovery and economic sustainability.
Increased international cooperation on science, technology and innovation is not only a moral imperative, for example regarding COVID vaccine development – it is in everyone’s interest.
Visit the documents and resources listed in the “Key Human Rights Guidance” below for more information.
Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR), art. 28: Everyone is entitled to a social and international order in which the rights and freedoms set forth in this Declaration can be fully realized.
International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR), art. 2.1: Each State Party to the present Covenant undertakes to take steps, individually and through international assistance and co-operation, especially economic and technical, to the maximum of its available resources, with a view to achieving progressively the full realization of the rights recognized in the present Covenant by all appropriate means, including particularly the adoption of legislative measures.
International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR), art. 11.1: The States Parties to the present Covenant recognize the right of everyone to an adequate standard of living for himself and his family, including adequate food, clothing and housing, and to the continuous improvement of living conditions. The States Parties will take appropriate steps to ensure the realization of this right, recognizing to this effect the essential importance of international co-operation based on free consent.
International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR), art. 15.1.b: The States Parties to the present Covenant recognize the right of everyone: (b) To enjoy the benefits of scientific progress and its applications.
International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR), art. 15.3: The States Parties to the present Covenant undertake to respect the freedom indispensable for scientific research and creative activity.
2. Enhance generation of disaggregated data (17.18)
Timely and reliable disaggregated data is critical for the ability to understand who is impacted by the pandemic and how, as well as to measure whether the COVID recovery is reaching and benefitting those left furthest behind in the line for the 2030 Agenda and human rights commitments.
Sustainable response and recovery actions:
National statistical offices should leverage all sources of data at their disposal and mobilize partners and experts from all sectors of society to implement solutions for the production of timely and disaggregated statistics.
Countries should invest in strengthening the capacity of national statistical offices and other data providers.
Countries with high statistical capacity should offer statistical capacity development support to countries with low capacity.
Countries should adopt a human rights-based approach to data collection. This involves ensuring participation in the data collection process, especially by the marginalized; data disaggregation to guard against discrimination; self-identification that does not reinforce further discrimination against vulnerable groups; transparency regarding the data collection process; privacy for respondents and maintaining confidentiality of their personal data; and accountability in data collection and use.
Visit the documents and resources listed in the “Key Human Rights Guidance” below for more information.
International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights Art 2.1: Each State Party to the present Covenant undertakes to respect and to ensure to all individuals within its territory and subject to its jurisdiction the rights recognized in the present Covenant, without distinction of any kind, such as race, colour, sex, language, religion, political or other opinion, national or social origin, property, birth or other status.
International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights Art 2.2: The States Parties to the present Covenant undertake to guarantee that the rights enunciated in the present Covenant will be exercised without discrimination of any kind as to race, colour, sex, language, religion, political or other opinion, national or social origin, property, birth or other status.
Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities
Art. 4.1:
States Parties undertake to ensure and promote the full realization of all human rights and fundamental freedoms for all persons with disabilities without discrimination of any kind on the basis of disability. To this end, States Parties undertake:
31.1
States Parties undertake to collect appropriate information, including statistical and research data, to enable them to formulate and implement policies to give effect to the present Convention. The process of collecting and maintaining this information shall:
31.1.a
Comply with legally established safeguards, including legislation on data protection, to ensure confidentiality and respect for the privacy of persons with disabilities.
31.1.b
Comply with internationally accepted norms to protect human rights and fundamental freedoms and ethical principles in the collection and use of statistics.
31.2
The information collected in accordance with this article shall be disaggregated, as appropriate, and used to help assess the implementation of States Parties' obligations under the present Convention and to identify and address the barriers faced by persons with disabilities in exercising their rights.
31.3
States Parties shall assume responsibility for the dissemination of these statistics and ensure their accessibility to persons with disabilities and others
Key Resources
- Global solidarity to fight COVID-19, General Assembly, Resolution, A/RES/74/270, 2020
- Comprehensive and coordinated response to COVID-19, General Assembly, Resolution, A/RES/74/306, 2020
- Humanitarian concerns and negative impact of unilateral sanctions and their exemptions during the COVID-19 pandemic, Special Rapporteur on the negative impact of the unilateral coercive measures on the enjoyment of human rights / Special Procedures, Guidelines, 2020
- Research Roadmap for the COVID-19 Recovery, United Nations, 2020
- UN COVID-19 Data Hub, United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA) Statistics, website
- Financing for Sustainable Development Report 2020, Inter-Agency Task Force on Financing for Sustainable Development, Report, 2020
- Recommendations from human rights monitoring mechanisms linked to SDG 17 by country, Danish Institute for Human Rights, search page
- Human rights law and standards linked to SDG 17 by target, Danish Institute for Human Rights, search page
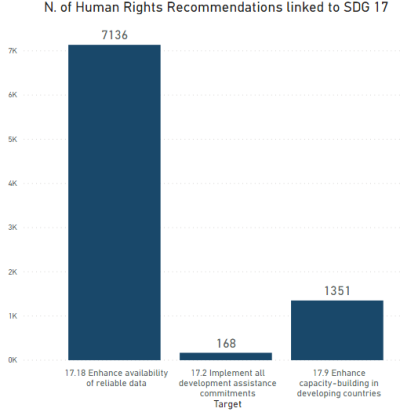
Explore all Recommendations from human rights monitoring mechanisms linked to SDG 17 by country

