SDG 13 and Sustainable Recovery

Key aspects of SDG 13:
1. Take urgent action to combat climate change (multiple targets under SDG 13)
The COVID-19 pandemic occurs amidst a wider planetary crisis caused by human-induced climate change. Although greenhouse gas emissions briefly dipped in 2020 due to travel bans and economic slowdowns resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic, the improvement turned out to be temporary. Greenhouse gas emissions reached around pre-pandemic levels again in 2021. As the global economy begins to recover from the pandemic, emissions are expected to return to higher levels. Drastic reductions are needed to avoid the worst consequences of runaway climate change.
The economic stimulus packages have so far not contributed sufficiently to accelerating the necessary transition required to meet the SDGs and the targets under the Paris Agreement on climate change. G20 nations have committed more COVID-19 recovery funds to fossil fuels than to clean energy according to the Energy Tracker Project. As of now the national climate pledges and other mitigation measures, would result in a temperature rise of 2.7 degrees, well above the Paris Agreement goal.
Sustainable response and recovery actions:
The recovery from COVID 19 must accelerate the transformation to green and sustainable economies rather than halt or reverse it based on short-term, narrow economic considerations.
To address the climate emergency, pandemic recovery plans need to trigger long-term, systemic shifts that will change the trajectory of CO2 levels in the atmosphere.
The UN Secretary-General has proposed six climate-positive actions for governments to take when building back their economies and societies:
- Green transition: investments must accelerate the decarbonization of all aspects of our economy.
- Green jobs and sustainable and inclusive growth.
- Green economy: making societies and people more resilient through a transition that is fair to all and leaves no one behind.
- Invest in sustainable solutions: fossil fuel subsidies must end, and polluters must pay for their pollution.
- Confront all climate risks.
- Cooperation – no country can succeed alone.
Visit the documents and resources listed in the “Key Human Rights Guidance” below for more information.
Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR). art. 3: “Everyone has the right to life, liberty and security of person”.
International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR), art. 6.1: “Every human being has the inherent right to life. This right shall be protected by law. No one shall be arbitrarily deprived of his life”.
Key Human Rights Guidance
-
COVID-19 materials from UNEP, United Nations Environment Programme, website
-
UN Guiding Principles on Human Rights and the Environment, Special Procedures, Report, 2018
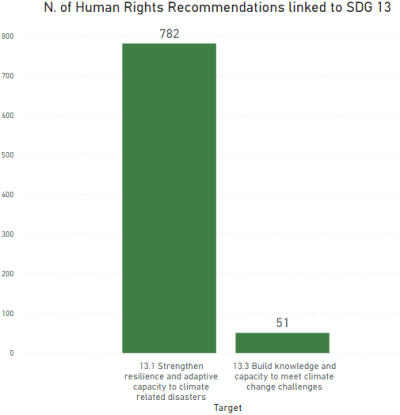
Explore all Recommendations from human rights monitoring mechanisms linked to SDG 13 by country

