SDG 1 and Sustainable Recovery

Key aspects of SDG 1 related to COVID-19
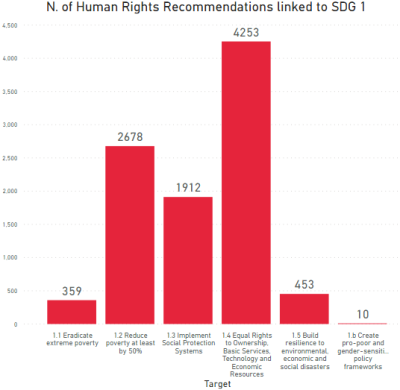
1. Eradicate extreme poverty, reduce poverty and ensure equal rights to economic resources (SDG targets 1.1, 1.2 and 1.4)
The economic recession caused by the COVID-19 pandemic has had and will continue to have significant impacts on global poverty levels. Because of COVID-19, extreme poverty rose in 2020 for the first time since 1997. The poorest 20% experienced the steepest decline in incomes during the pandemic, and in 2021 the poorest 40% still haven’t started to recover from their income loses. According to the World Bank, on average COVID-19 has set back global poverty reduction by 4 years, and whilst it was estimated that 588 million would live in extreme poverty by 2030, this figure has risen by 50 million as a result of the pandemic.
The pandemic has exposed and exacerbated existing inequalities in access to resources and services within and between countries.
Sustainable response and recovery actions:
The situation calls for a transformation of the economic structures to put the needs of the excluded first, with human rights at the heart of economic policies and choices. Ensuring minimum wages, equal access to economic resources (including land), financial and basic services as well as new technologies must be key priorities.
Countries should strive for triple dividend measures that create decent jobs for people who are poor while reducing ecological footprint and expanding access to essential goods and services, thereby also fulfilling basic needs and human rights.
Visit the documents and resources listed in the “Key Human Rights Guidance” below for more information.
Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR), art. 3: Everyone has the right to life, liberty and security of person.
International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR), art. 11.1: The States Parties to the present Covenant recognize the right of everyone to an adequate standard of living for himself and his family, including adequate food, clothing and housing, and to the continuous improvement of living conditions. [...]
Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW), art. 13: States Parties shall take all appropriate measures to eliminate discrimination against women in other areas of economic and social life in order to ensure, on a basis of equality of men and women, the same rights, in particular (13.a) The right to family benefits; (13.b) The right to bank loans, mortgages and other forms of financial credit.
International Labour Organisation (ILO) C122 Employment Policy Convention: This ILO governance Convention aims at stimulating economic growth and development, raise levels of living, meet manpower requirements and overcome unemployment and underemployment.
International Labour Organisation (ILO) C131 Minimum Wage Fixing Convention: This ILO Convention requires ratifying states to establish a minimum wage fixing machinery capable of determining and periodically reviewing and adjusting minimum wage rates having the force of law.
2. Implement social protection systems and build the resilience of the poor (SDG targets 1.3, 1.5)
The COVID-19 pandemic has caused millions of people to lose their jobs and livelihoods overnight. The pandemic has disproportionally affected those not covered by adequate national social protection systems.
Sustainable response and recovery actions:
Sustainable recovery must include strengthening progress towards universal social protection, building on the increase of coverage during the COVID-19 response, redesigning social protection systems so they are more responsive to shocks, including climate shocks, and strengthening care systems so they respond to the needs of all genders throughout their lifecycle. Redesigning social protection is not only an investment in local economies, but also contributes to growth and resilience in times of crisis.
Visit the documents and resources listed in the “Key Human Rights Guidance” below for more information.
International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR), art. 9: The States Parties to the present Covenant recognize the right of everyone to social security, including social insurance.
Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC), art 26.1: States Parties shall recognize for every child the right to benefit from social security, including social insurance, and shall take the necessary measures to achieve the full realization of this right in accordance with their national law.
International Labour Organisation (ILO) C102 Social Security (Minimum Standards) Convention: Each Member for which this Part of this Convention is in force shall secure to the persons protected the provision of [medical care benefit], [sickness benefit], [unemployment benefit], [old-age benefit], [employment injury benefit], [family benefit], [maternity benefit], [invalidity benefit], [survivors' benefit], in accordance with the following Articles of this Part.
International Labour Organisation (ILO) R202 Social protection Floors Recommendation: This provides guidance to Members to: (a) establish and maintain, as applicable, social protection floors as a fundamental element of their national social security systems; and (b) implement social protection floors within strategies for the extension of social security that progressively ensure higher levels of social security to as many people as possible, guided by ILO social security standards.
Key Human Rights Guidance:
- Right to social security, International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR), General Comment, No. 19 (E/C.12/GC/19), 2008
- Extreme Poverty and Human Rights, Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR), Guiding principles
- Looking back to look ahead: A rights-based approach to social protection in the post-COVID-19 economic recovery, the Special Rapporteur on extreme poverty / Special Procedures, unofficial report, 2020
- The “just transition” in the economic recovery: eradicating poverty within planetary boundaries, UN Special Procedures, Report, 2020
- Observations by ILO Supervisory Bodies on the ILO instruments (by convention and by country), International Labour Organisation (ILO), search page
- Social Security, International Labour Organisation (ILO), General Survey, 2011
- Social Protection Floors, International Labour Organisation (ILO), General Survey Recommendation, No. 202, 2012
- Recommendations from human rights monitoring mechanisms linked to SDG 1 by country, Danish Institute for Human Rights, search page
- Human rights law and standards linked to SDG 1 by target, Danish Institute for Human Rights, search page